Tierimpfungen: Fremdproteine verursachen Häufung von Impfkomplikationen
Tierimpfungen: Fremdproteine verursachen Häufung von Impfkomplikationen
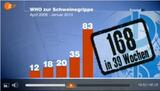
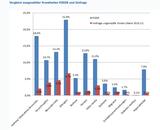
(ir) Eine im Juli 2007 in der Zeitschrift "Journal of Comparative Pathology" vorgestellte Studie zeigte, dass Impfstoffe ohne Fremdeiweiße bei neugeborenen Kätzchen und Welpen weniger Impfkomplikationen hervorrufen als Impfstoffe, die z.B. Albumin aus Rinderblut enthalten.
Vaccine safety in the neonatal period.
J Comp Pathol. 2007 Jul;137 Suppl 1:S51-6
Authors: Day MJ
Administration of two doses of multicomponent vaccine to pups and kittens between 8 and 16 weeks of age has become a standard and important part of veterinary healthcare for this susceptible neonatal population.
Currently available vaccine formulations conform to high standards of quality, safety and efficacy, but there remains a very small risk of adverse effect following vaccination.
Quantifying this risk is extremely difficult and there are few meaningful data available.
It would seem, however, that there is a higher prevalence of suspected adverse reactions (SARs) following vaccination in the neonatal period than in adult animals.
The range of reported adverse reactions in neonates is broad, and includes: suspected lack of efficacy, mild non-specific and transient illness post-vaccination, and the development of hypersensitivity or autoimmune reactions.
The most common reactions in both species are the various clinical manifestations of type I hypersensitivity.
These events might relate to the induction of IgE antibody specific for extraneous protein incorporated within vaccines, in particular bovine serum albumin.
That such reactions are most prevalent in small breed dogs, that also make the highest serological responses to vaccination, suggests a case for the formulation of low-dose products for miniature breeds.
At least a proportion of neonatal vaccine SARs are related to the use of potent immunological adjuvants in certain products.
A recent study in neonatal kittens has confirmed that non-adjuvanted vaccine induces significantly less local vaccine site inflammation than comparable adjuvanted products.
The low risk of vaccine SARs in early life may therefore be further reduced by formulating non-adjuvanted vaccines with reduced content of extraneous protein, and by carefully considering the optimum vaccination protocol for any individual animal.
Journal of Comparative PathologyVolume 137, Supplement 1, July 2007, Pages S51-S56
Proceedings from The Merial European Vaccinology Symposium (MEVS) - Athens, Greece, 2-4 November 2006.